
Good Nutrition, Better Learning: Tips To Help Children Eat Well.
What children eat in their early years can have an impact on their health in the years to come. Giving your children an early start in healthy eating is not only great for their growth, but also beneficial for their brain development. Studies show that good nutrition greatly influences concentration and learning, especially in children.
How Good Nutrition Influences Children’s Learning

Children need to be healthy to enjoy a fulfilling learning experience. A healthy body gives them the energy to participate in learning activities and a strong mind helps them to concentrate during lessons. Here are the importance of good nutrition in children’s learning:
- Supports children’s early brain development
- Influences children’s behaviour, mood and concentration
- Good nutrition makes children healthier. Studies show that a healthy breakfast is linked to improved cognitive function (especially memory), less absenteeism and better mood.1-3
- There are certain nutrients that are particularly good for brain function and development, such as iron, zinc, magnesium and iodine; vitamin D; B vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids.4
- Good gut health is known to have a positive effect on mood and attention. This may be why, according to studies, children have been shown to score better at tests involving memory and attention, two hours after a high fibre breakfast cereal, compared to those who consume a high sugar, low fibre one. Dietary fibre can be found from plant-based foods such as vegetables, fruits, wholegrain cereals, nuts, beans and pulses.4
Now, on to the interesting part: Getting the kids to eat healthy! Whether your children are good eaters or picky little ones, getting them to eat healthy on a daily basis can be quite a challenge. But fret not, because we have some useful tips that we think might just do the trick!
10 Tips To Encourage Your Children To Eat Well and Practice Good Eating Habits
- Have regular meals together
It’s always more fun to eat together. Often, younger children get excited about what mum's cooking for dinner tonight, so surprise them with their favourite meals every now and then. Family meals are also a great time for parents to introduce new foods and to model healthy eating.
Serve a varied diet
Our bodies require different nutrients (as opposed to single nutrients) to support our brain functions. Not sure where to begin? Just follow the Malaysian Food Pyramid 2020 based on your children’s age: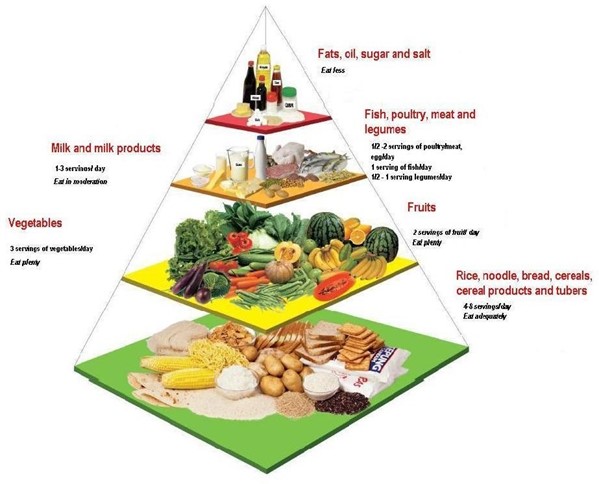
- Avoid using food as a punishment or reward
Punishing children by withholding their meals might cause them to worry about not getting enough food, so they may try to eat whenever they have the chance. On the other hand, rewarding them with “special” food such as chips or sweets might make them think that these “treats” are better food compared to other regular foods.
- Involve children in meal planning
Take your children grocery shopping with you and show them the variety of foods available. Ask them what they would like you to cook for the week.
Choose the ingredients together and take this opportunity to teach them about nutrition. This gives them a sense of accomplishment, and also appreciation for the food that they eat.
- Train children to drink more water
Always offer water before any other drinks. Over consumption of sweetened drinks will increase the risk of diabetes in children.
- Eat at the dining table ONLY
Practise having meals only at the dining table, without any distractions such as gadgets. Letting children eat in front of the TV or while watching a video on the tablet/phone is not only hazardous as it increases the risk of choking (not paying attention to the food), but may also make it difficult for children to realise the feeling of fullness, hence leading to overeating.
- Be good role models
Your children will follow your lead. So if you want them to eat well and healthy, you have to show them how it’s done. Avoid fussing about your personal body struggles in front of the children as it may have a negative influence on their perspective of an ideal body image.
- Serve appropriate portions
When in doubt, always refer to the recommended daily food serving guideline by the Ministry of Health Malaysia. However, teach your children to acknowledge the feeling of fullness and allow them to stop eating when they feel full. You don’t want them to feel “punished” by forcing them to empty their plates.
- Stock up on healthy foods
Load your pantry with different kinds of “real foods” such as fruits, vegetables, low-fat yogurt, low-fat milk, whole grain breads and cereals, etc. Tip: Prepare a snack cart and fill it with fruits and a variety of healthy snacks. Add in chocolates and candies once in a while so they don’t feel deprived.
- Cook with your children
Make fruit smoothies, breads, oatmeal pancakes served with fresh fruits, vege chips and many other interesting healthy recipes together. Show your children that healthy food does not have to be boring.
Bear in mind that you have to be consistent in carrying out these tips. Allow for trial and error as every child is unique. It’s going to take some effort and a whole lot of patience, but in time, you will start to see the benefits of good nutrition in your children’s behaviour and learning performance.
Supporting Children’s Learning Performance With Appropriate Nutrients For Brain Development
You’ve already nailed down your to-do list to encourage your children to eat better. Now how about an extra tip on how to supplement your children’s daily diet to optimise their brain development in early childhood?
Provide them with essential nutrients such as sphingomyelin, DHA, 2’-FL and Oligofructose.
Studies show that essential nutrients such as DHA and sphingomyelin, are the force behind brain connections.
Sphingomyelin is the backbone of myelination and supports efficient brain connections.5-7

- Myelination is one of the major processes that guides brain development in early childhood onwards. Myelination happens when a substance made of fatty lipids and protein called myelin, coats the nerve fibre (this is where messages are transmitted between neurons) in the brain. This coating is called the myelin sheath, and sphingomyelin is a phospholipid that is an integral component of the myelin sheath.8
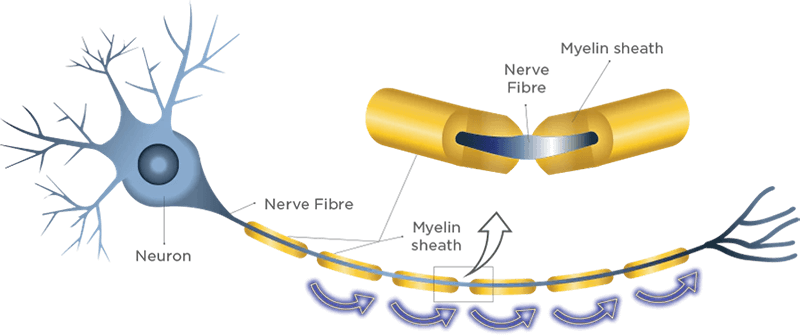
The myelination process.
Support children to learn faster and explore a world of amazing discoveries by providing them with good nutrition from their early years.
S-26 GOLDⓇ PROGRESSⓇ is now formulated with innovative ingredients to provide our most advanced formulated milk for children.
S-26 GoldⓇ ProgressⓇ is specially formulated with sphingomyelin, DHA, 2’-FL and oligofructose. Support your child’s growth with appropriate nutrition and sufficient rest to help him Think Quick and Learn Fast.
Disclaimer: This content is shared for informational purposes only and not intended to be a substitute for professional/medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. We recommended that you always seek the advice of your healthcare professional for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition/specific situation.
References:
- Taras HL. Nutrition and student performance at school. Journal of School Health. 2005;75:199–213.
- Rampersaud GC, Pereira MA, Girard BL, et al. Breakfast habits, nutritional status, body weight, and academic performance in children and adolescents. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2005;105:743–760.
- Hoyland A, Dye L, Lawton CL. A systematic review of the effect of breakfast on the cognitive performance of children and adolescents. Nutrition Research Reviews. 2009;22:220–243.
- https://www.bda.uk.com/resource/diet-behaviour-and-learning-children.html
- Henríquez-Henríquez MP, Solari S, Quiroga T, Kim BI, Deckelbaum RJ, Worgall TS. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:300.
- Tanaka K, Hosozawa M, Kudo N, et al. Brain Dev. 2013;35(1):45-52.
- Deoni S, Dean D 3rd, Joelson S, O’Regan J, Schneider N. Neuroimage. 2018;178:649- 59.
- Salzer JL, Zalc B.Curr Biol. 2016;26:R971-R975.
Other sources:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/brain-food-for-kids
- https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/habits.html?ref=search
- https://www.webmd.com/children/kids-healthy-eating-habits
- https://www.publichealth.hscni.net/sites/default/files/Nutrition%20Matters%20 for%20the%20early%20years%200118.pdf
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/nutrition/facts.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4981537/

